4 of the Best Over-the-Counter Back Pain Pills According to Experts
Often people don't think of the risks of taking over-the-counter pain medicine (OTC). However, a survey by the American Gastroenterological Association found more than 2 out of 5 people don't follow label instructions, thus increasing risks of problems.
That same survey discovered 3 in 10 people experienced serious complications due to overdosing on OTC pain medicines.
Selecting the best pain relief becomes even more challenging when we're presented with so many options: aisles of pills at the drugstore, advertisements promising to reduce pain, and differing opinions of friends and family.
You may have acute or chronic back pain. You may have neck pain or low back pain. The question is, “What's the most effective and safest option for your unique back pain?”
Here's the breakdown:
Prescription Pills For Back Pain
As you know, there are both prescription and OTC pills for back pain. And, you’ve probably heard a lot about prescription pain medicines in the news. Although the focus here is on OTC pain pills, it might be helpful to know some of the facts about prescription pills for back pain. It might help you better understand why OTC pills are usually a better, safer choice.
There are many types of prescription medicines used to treat back pain - many in pill form. Some are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs. They’re similar to Aleve Back & Muscle Pain tablets, Advil Liqui-Gels, and Motrin PM that you’ll read about below.
Most of the prescription pain pills are narcotics - this means that they act on the central nervous system, the brain, nerve pathways, and spinal cord. Although they work well in the short term to relieve back pain, they have many side effects, are potentially dangerous, and can lead to dependence and addiction.
Over time, narcotics may also lead to tolerance. This means you have to take higher doses to get the same effect. This further increases dependence and addiction risks, as well as some serious side effect risks.
Opioids are generally categorized as narcotics and are prescribed for pain relief in some situations. You may be familiar with some of the common side effects of opioids like sedation, nausea, and constipation (one of the most common side effects with a specific name - opioid-induced constipation).
Less common side effects include heightened sensitivity to pain, immune system dysfunction, rigid muscles, and spasms of the muscles. The side effects are serious and some of them are actually pain-causing. Isn’t the idea to reduce back pain and feel better?
Opioids like hydrocodone, oxycodone, morphine, and fentanyl have become familiar to many of us. The use of opioids in the U.S. is a national crisis with high levels of misuse, rising numbers of overdoses (made worse by the pandemic), and states suing pharmaceutical companies and drug store chains for their involvement.
This brings us back to OTC pain pills. You are much less likely to have problems with OTC pain pills. Although they need to be used carefully and have potential side effects, they are in most cases, a better, safer choice.
How Do OTC Pain Medicines Work?
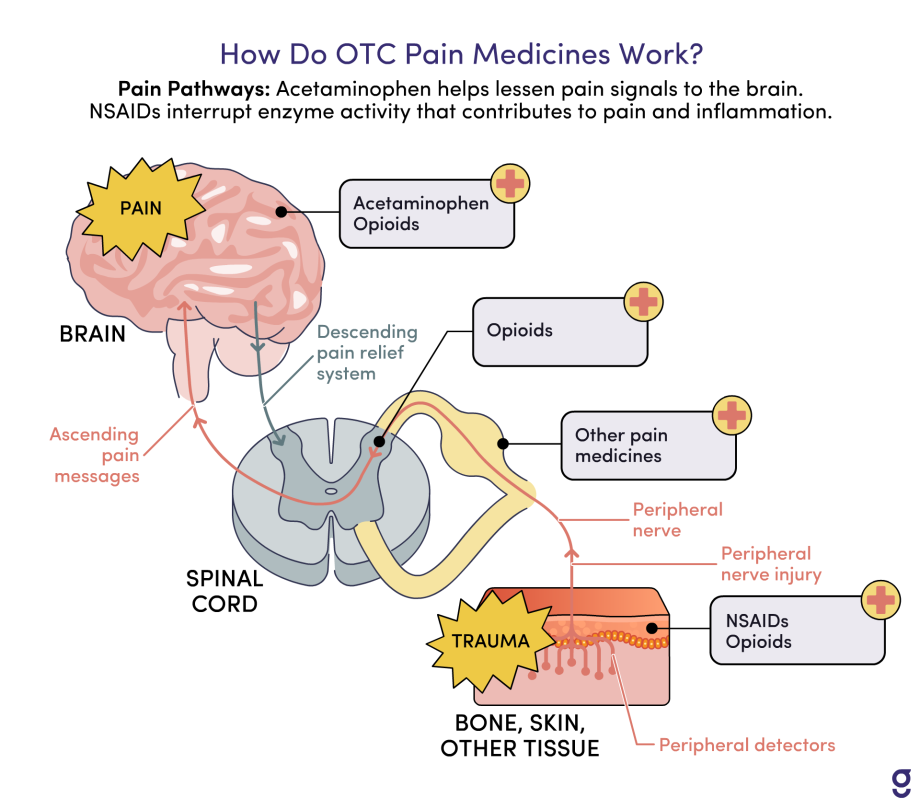
Pain Pathways: Acetaminophen helps lessen pain signals to the brain. NSAIDs interrupt enzyme activity that contributes to pain and inflammation.
Here are some of the best OTC back pain medicines on the market, according to experts:
For All-Day Relief: Aleve Back & Muscle Pain
Works for: 12 hours
Dosage: 220 mg naproxen sodium
Why experts recommend it:
The formula is specifically used to treat pain in the back and muscles back pain and muscle pain. One tablet lasts for up to 12 hours – a great option for those who suffer from all-day pain.
How it works:
Aleve is a type of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug or NSAID. It works by limiting the overproduction of chemicals called prostaglandins. Prostaglandins play a role in inflammation, pain, and fever. The generic names for two common OTC NSAIDs are ibuprofen and naproxen sodium.
How to use Aleve Back & Muscle Pain tablets:
Use as directed on the label or as instructed by your doctor
Do not take more than three tablets in 24 hours
If NSAIDs cause you to have gastrointestinal problems, try taking them with food
Aleve (naproxen sodium) is not meant for long-term use – it can be used for up to ten days
For Fast Relief: Advil Liqui-Gels
Works for: 6 to 8 hours
Dosage: 200 mg ibuprofen
Why experts recommend it:
The solubilized ibuprofen in the capsules is more easily absorbed into the bloodstream. This leads to faster relief. The capsule form also makes it easier to swallow.
How it works: Advil Liqui-Gels contain ibuprofen, another nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Ibuprofen’s effects do not last as long as naproxen sodium (Aleve). However, it may be less harsh on the gastrointestinal system. Evidence from a 2016 study showed that liquid gels may provide faster pain relief than tablets.
How to use Advil Liqui-Gels:
Use as directed on the label or as instructed by your doctor
Do not exceed 6 capsules in 24 hours unless instructed by a doctor
If NSAIDs cause you to have gastrointestinal problems, try taking them with food
Precautions when taking NSAIDs (ibuprofen and naproxen sodium):
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can increase the chance of serious gastrointestinal problems such as ulcers, bleeding, inflammation, and perforations.
People who take NSAIDs (other than aspirin) such as naproxen and ibuprofen, may have a higher heart attack or stroke risks than people who do not take these medications. People with kidney problems, or those who have had coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery, should not take NSAIDs.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug side effects:
Ask a medical professional if you have any questions about taking NSAIDs.
Common, mild side effects of NSAIDs:
Gas
Bloating
Heartburn
Abdominal pain
Call your doctor if these symptoms appear for more than a few days or worsen with time.
Severe side effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs:
If you have any of the following problems, it is crucial to seek medical attention or call your doctor right away. These include but are not limited to:
Severe abdominal pain
Any signs of bleeding, such as bloody or red-dark stools, blood in urine, vomiting blood or vomit that looks like coffee grounds, abnormal bloody vaginal discharge, bleeding gums, or any other persistent abnormal bleeding
Swelling of the face, eye area, lips, tongue, hands, ankles, or feet
Blurred vision
Yellowing of the skin or whites of eyes (jaundice)
Chest pain
Red or irritated eyes
Skin problems such as red, very dry, blistered, painful, or peeling skin (with or without fever)
For Osteoarthritis Relief: Tylenol Regular Strength
Works for: 4 to 6 hours
Dosage: 325 mg acetaminophen
Why experts recommend it:
Tylenol is a good alternative for those who have any underlying conditions in which a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug would not be appropriate. It is an effective pain reliever with fewer side effects than NSAIDs.
There are also stronger formulations with higher doses of acetaminophen, such as extra-strength Tylenol. They are specifically designed for arthritis pain relief. Higher doses have greater risks of side effects and serious problems.
How it works:
Acetaminophen is an analgesic, also known as a general pain reliever, but it isn’t anti-inflammatory. Evidence shows acetaminophen works by changing the way our brains perceive pain.
How to use Tylenol Regular Strength:
Use as directed on the label or as instructed by your doctor
Do not take more than 10 tablets in 24 hours, unless told by a doctor
Not recommended for use for over ten days unless directed by a doctor
Precautions when taking Tylenol:
Acetaminophen can cause serious liver problems with high, frequent, or long-term dosing. Do not take acetaminophen if you:
Have a history of liver disease
Drink more than three alcoholic beverages per day
Are allergic to acetaminophen or any of the other ingredients
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, ask your doctor before using acetaminophen
Are taking any other medication containing acetaminophen. This may cause permanent liver damage
Common side effects of acetaminophen:
Nausea and/or vomiting
Problems sleeping
Abdominal pain
Loss of appetite
Headache
If you have any of the following side effects, it is crucial to seek medical attention or call your doctor right away. These include, but are not limited to:
Severe abdominal pain
Yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes (jaundice)
Itching or swelling (especially of the tongue or throat)
Severe dizziness
Problems breathing
OTC pain medications are only one part of managing your pain. At Goodpath, we use a well-rounded approach that includes therapeutic exercise, nutritional support, and mind-body techniques like meditation or yoga. Start by taking our assessment to get your individualized program.
For Nighttime Relief: Motrin PM
Works for: 8 to 12 hours
Dosage: 200 mg ibuprofen and 38 mg diphenhydramine citrate
Why experts recommend it:
The two active ingredients in Motrin PM help when you have trouble sleeping due to pain.
How it works:
Diphenhydramine is an antihistamine used to help relieve allergy symptoms. There is evidence that Some types of antihistamines can cause drowsiness, which helps a person sleep better or fall asleep faster.
How to use Motrin PM:
Use as directed on the label or as instructed by your doctor
If NSAIDs cause you to have gastrointestinal problems try taking them with food
Precautions when taking Motrin PM:
Do not take Motrin PM for longer than 10 days or at higher doses unless instructed by your doctor
People who take NSAIDs (other than aspirin) may have a higher heart attack or stroke risks than people who do not take these medications
Do not drive or operate heavy machinery due to drowsiness from diphenhydramine
There are increased risks of falls for those over 65 years of age; do not take unless directed by your doctor
Common side effects of Motrin PM:
Nausea
Drowsiness
Loss of appetite
Chest congestion
More serious side effects of Motrin PM:
Dizziness
Temporary loss of hearing
Blurred vision
OTCs and Integrative Medicine for Back Pain
Integrative medicine combines conventional treatment (like OTC pills, creams, patches, prescriptions, exercise therapy, etc.) with complementary therapies.
Complimentary methods include nutritional supplements, relaxation, meditation, etc. It focuses on the whole person, as opposed to the specific problem. There is considerable evidence that integrative care has a positive effect on many areas of a person’s health and overall well-being, including decreased pain.
How Goodpath Can Help
OTC pain medicines usually work well to relieve pain and discomfort, however, you may want to consider additional combining them with other treatments.
At Goodpath, we use the integrative approach that may include OTC medicines, but also supplements, mind-body therapies, specific exercises, and nutritional support.
Take our quick assessment now. From there we will create a treatment plan specifically for you and your needs.
